Prerequisites
Before you begin, make sure you have:- A JBoss/WildFly application server running on a Linux system with administrative access.
- A certificate profile configured with the ACME enrollment method in Infisical.
- Network connectivity from your JBoss/WildFly server to Infisical.
- Port 80 open and reachable for ACME HTTP-01 validation.
- Java Development Kit (JDK) installed for keystore management tools.
Guide
Obtain ACME Configuration from Infisical
Navigate to your certificate management project in Infisical and locate your certificate profile configured with the ACME enrollment method. Click the Reveal ACME EAB option to view the ACME configuration details.
Click the Reveal ACME EAB option to view the ACME configuration details.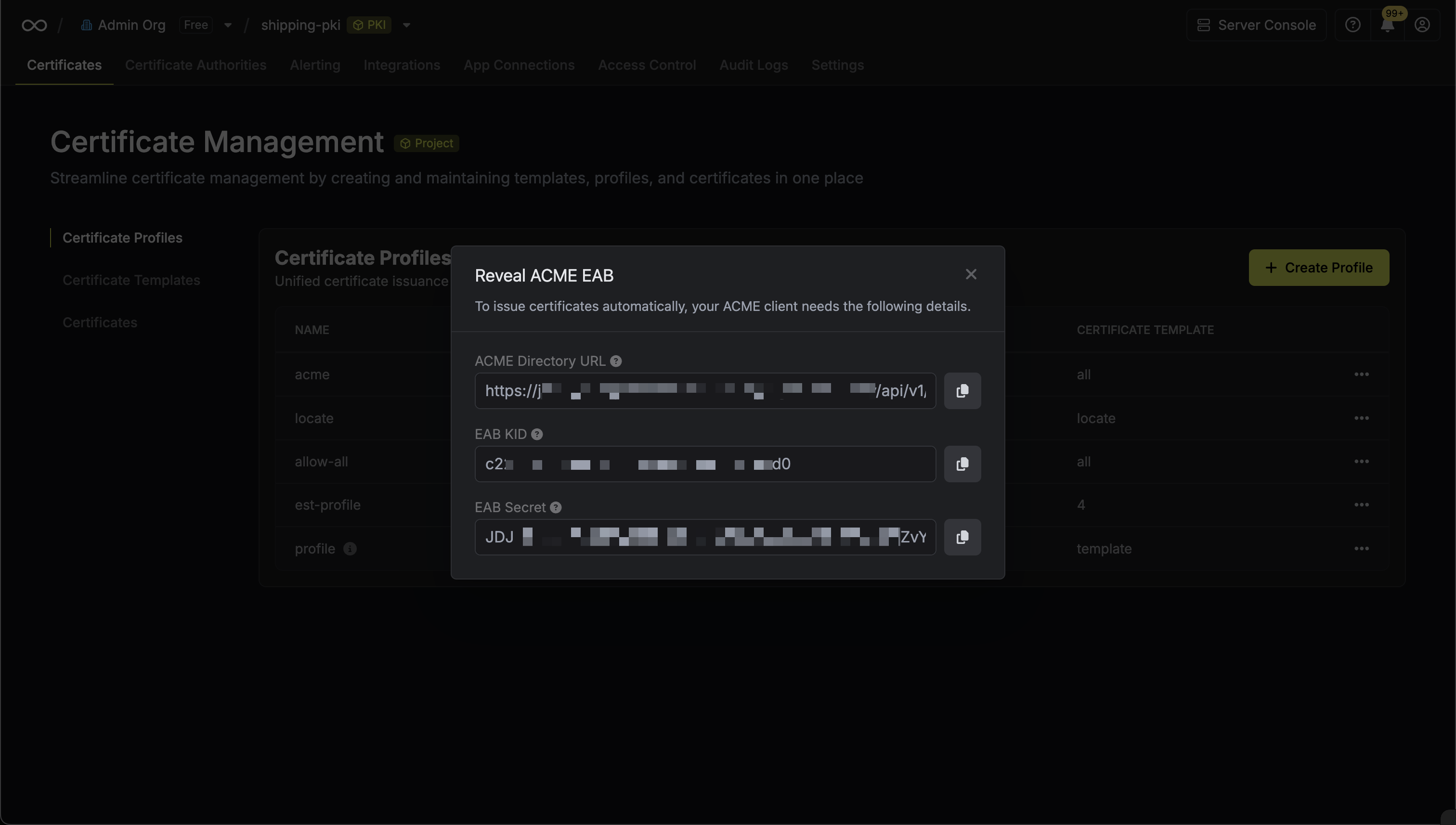 From the ACME configuration, gather the following values:
From the ACME configuration, gather the following values:
 Click the Reveal ACME EAB option to view the ACME configuration details.
Click the Reveal ACME EAB option to view the ACME configuration details. From the ACME configuration, gather the following values:
From the ACME configuration, gather the following values:- ACME Directory URL: The URL that Certbot will use to communicate with Infisical’s ACME server. This takes the form
https://your-infisical-instance.com/api/v1/cert-manager/certificate-profiles/{profile-id}/acme/directory. - EAB Key Identifier (KID): A unique identifier that tells Infisical which ACME account is making the request.
- EAB Secret: A secret key that authenticates your ACME client with Infisical.
Keep your EAB credentials secure as they authenticate your ACME client with Infisical PKI. These credentials are unique to each certificate profile and should not be shared.
Install Certbot
Install Certbot on the server where JBoss/WildFly is running by following the official Certbot installation guide.The installation guide provides up-to-date instructions for various Linux distributions and package managers, ensuring you get the most current version of Certbot.After installation, you can verify that Certbot has been installed correctly by running:
Request Certificate Using Certbot
Since JBoss/WildFly doesn’t have a native Certbot plugin, use the standalone authenticator to obtain certificates. Important: You must stop JBoss/WildFly before running this command as Certbot needs to bind to port 80 for the HTTP-01 challenge.Stop your JBoss/WildFly server:Run the following command to request a certificate from Infisical:For guidance on each parameter:
certonly: Instructs Certbot to request a certificate without modifying your JBoss/WildFly configuration; this mode is recommended because JBoss/WildFly requires certificates in Java keystore format rather than the PEM format that Certbot provides.--standalone: Uses Certbot’s standalone authenticator to solve the HTTP-01 challenge by starting a temporary web server on port 80.--server: The Infisical ACME directory URL from Step 1. This instructs Certbot to communicate with Infisical’s ACME server instead of Let’s Encrypt.--eab-kid: Your External Account Binding (EAB) Key Identifier from Step 1.--eab-hmac-key: The EAB secret associated with the KID from Step 1.-d: Specifies the domain name for which the certificate is being requested.--email: The contact email for expiration notices and account recovery.--agree-tos: Accepts the ACME server’s Terms of Service.--non-interactive: Runs Certbot without prompting for user input (recommended for automation).
/etc/letsencrypt/live/{domain-name}/.Because JBoss/WildFly requires certificates in Java keystore format, you’ll need to convert the PEM certificates provided by Certbot in the next step.Convert Certificate to Java Keystore
JBoss/WildFly requires certificates in Java keystore format rather than the PEM format provided by Certbot. Convert the PEM certificates to PKCS#12 format, which is supported by modern JBoss/WildFly versions.Create a PKCS#12 keystore from the PEM files:Set appropriate file permissions for security:You will need to configure JBoss/WildFly to use the new keystore. This process varies depending on your JBoss/WildFly version and security configuration (legacy security realms vs. Elytron subsystem). Refer to your JBoss/WildFly administration guide for specific SSL/TLS configuration steps.
Replace
changeit with a strong password and adjust the WildFly installation path based on your environment. Modern WildFly versions support PKCS#12 keystores directly, while older versions may require conversion to JKS format using the keytool utility.Verify Certificate Installation
After configuring JBoss/WildFly SSL, verify that your certificate was issued correctly and the keystore was created properly.Check that the certificate files were created by Certbot:You should see files like:Test the keystore contents (optional):Once you’ve configured JBoss/WildFly to use the keystore and restarted the service, you can verify HTTPS is working by accessing your application over SSL.
cert.pem(your certificate)chain.pem(certificate chain)fullchain.pem(certificate + chain)privkey.pem(private key)
Renew Your Certificate with Certbot
Unlike standard web servers, JBoss/WildFly certificate renewal requires additional steps because certificates must be converted to Java keystore format and the application server must be restarted to use the new certificates.To test the renewal process without affecting your live certificates, run the following command:This command simulates the full renewal process without modifying your active certificate. If the dry run succeeds, the renewal mechanism itself will work as expected.For actual renewal, since JBoss/WildFly requires the standalone authenticator, you’ll need to stop the server, perform the renewal, convert the certificate, and restart:To automate this process, you can create a renewal script. Create Make the hook executable:
/etc/letsencrypt/renewal-hooks/deploy/jboss-renewal.sh:Certbot automatically renews certificates when they are within 30 days of expiration using its built-in systemd timer. The deploy hook above will run after each successful renewal, handling the keystore conversion and service restart automatically. Because JBoss/WildFly requires the standalone authenticator (which stops the service temporarily), plan for brief service interruptions during renewal.

